Hint: This website is not optimized for your browser version.
End of coal power as part of the energy transition
Coal phase-out under KVBG Act
11 October 2021 - The decision to phase out coal was sealed on 3 July 2020 when the Bundestag and Bundesrat adopted the Act to Reduce and End Coal-Fired Power Generation (KVBG).
The legislation requires coal-fired electricity production in Germany to be reduced gradually and to stop at the latest at the end of 2038. It also requires the process of reducing coal power to be socially acceptable and as consistent as possible. The overarching aim is to guarantee a secure, low-priced, efficient and environmentally compatible supply of electricity for the general public (see section 2(1) KVBG).
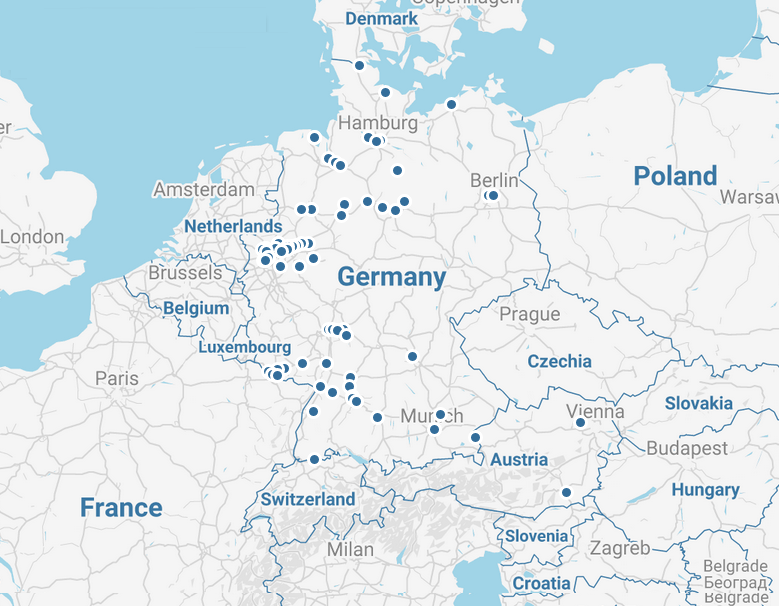
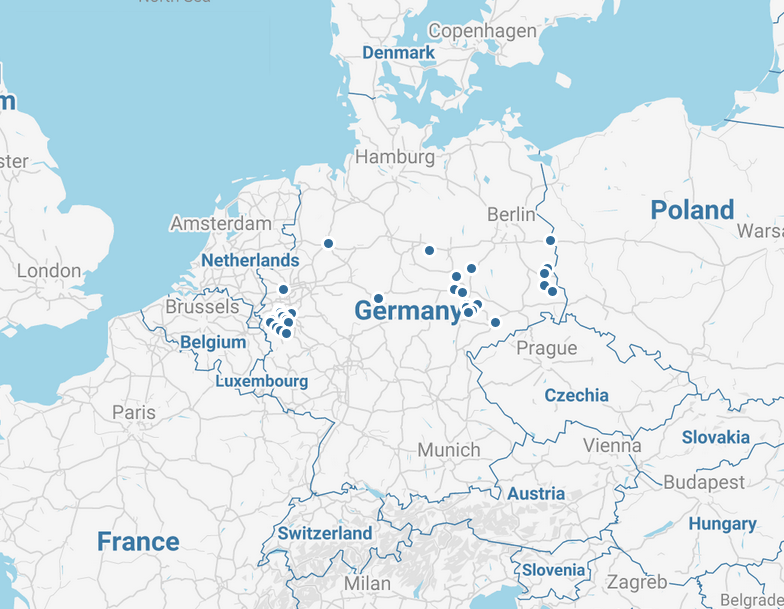
On the SMARD website you can view the figures for electricity generation from coal for the current day and previous periods (in the Market data visuals section) and you can see how many coal-fired power plants are or have been operating in Germany and how much electricity each plant has generated – even if a plant has already been shut down. You can see a map showing the locations of all the generation units in the "German electricity market" section and can use the "energy resources" drop-down list to select and view the units generating with hard coal or lignite.
The maps below show some of the power plants in Germany that use hard coal or lignite.
The capacity of hard coal-fired and lignite-fired power plants is set to decrease from the total of around 40 gigawatts (GW) in 2020 to 15 GW each by the end of 2022 (see section 4(1) and (2) KVBG).
Year | Net rated capacity (lignite and hard coal) |
2020 | Approx 40 GW |
End of 2022 | 30 GW |
End of 2030 | 17 GW |
2038 | 0 GW |
The capacity is set to drop further to 8 GW for hard coal-fired plants and 9 GW for lignite-fired plants by the end of 2030. This process will continue until electricity generation from hard coal and lignite finally stops in 2038.
The processes to reduce capacity are different for large lignite-fired plants and for hard coal-fired and small (up to and including 150 MW net rated capacity) lignite-fired plants.
While the legislation sets the final closure dates and compensation for large lignite-fired power plants, it provides for a tendering process to achieve the gradual reduction in capacity for hard coal-fired and small lignite-fired power plants.
Plant operators can participate in the tendering carried out by the Bundesnetzagentur by bidding a price per megawatt (MW) of reduced capacity. The legislation sets a maximum price for each round of tendering, so it is not possible for plant operators to bid any price they want.
Four of the seven scheduled rounds have now been completed and have ensured that the phase-out targets up to the end of 2022 will be or have been met. Operators of hard coal-fired power plants can compete for a tender in the remaining three rounds. The deadline for bids in the fifth round is 1 March 2022.
Operators that are awarded a tender in a round are paid the price bid per megawatt of reduced capacity; if the price bid is higher than the maximum for the round, it is capped to the maximum price allowed.
The plants that are awarded a tender in a round must stop coal-fired generation from a certain date. Some plants are exempted from shutdown: plants that are part of the capacity reserve (section 13e of the Energy Industry Act – EnWG), and plants that the transmission system operators have identified as important for the system and that have been confirmed as such by the Bundesnetzagentur. Power plants that are designated as important for the system remain available as grid reserve power plants for a certain period of time to safeguard the electricity grid in critical situations and maintain the voltage in the grid.
If any of the rounds for the target date of 2024 and onwards are undersubscribed, and at the latest after the last round of tendering for the target date of 2026, the "statutory reduction" process will apply for any volume remaining after tenders have been awarded. The Bundesnetzagentur will then use a ranking list to decide which hard coal-fired and small lignite-fired power plants will need to stop using coal and when, unless plant operators decide to do so voluntarily. Operators of plants required to stop coal-fired operation in the statutory reduction process will not receive any direct compensation.
The Bundesnetzagentur undertakes a wide range of tasks in implementing the coal phase-out. Details of the tendering rounds, the applicable deadlines and the tenders awarded (including the capacity and compensation) can be found in the relevant section of the Bundesnetzagentur's website.